Подписывание кода
Code signing is a security technology to certify that an app was created by you. You should sign your application so it does not trigger any operating system security warnings.
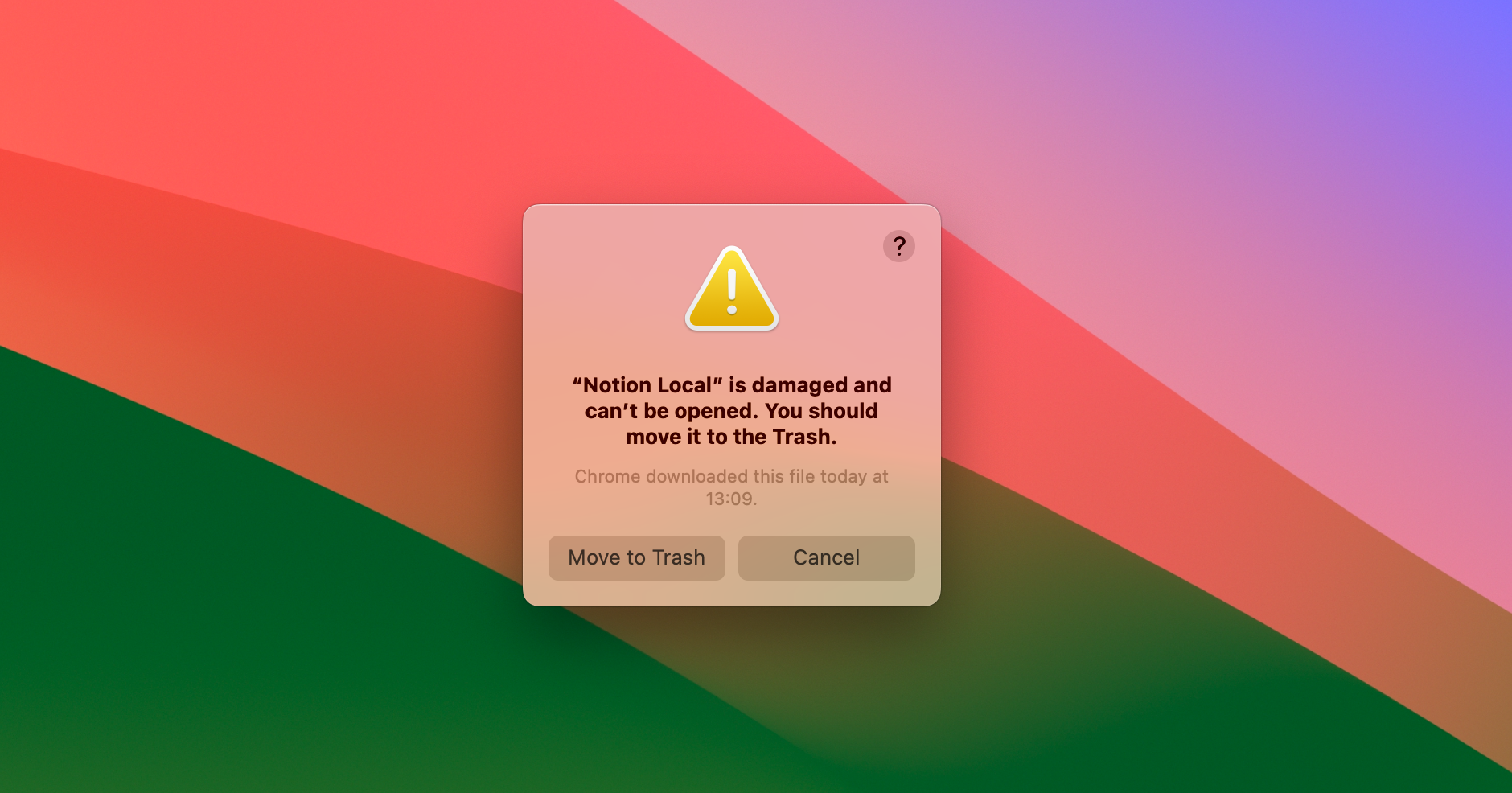
Both Windows and macOS prevent users from running unsigned applications. It is possible to distribute applications without codesigning them - but in order to run them, users need to go through multiple advanced and manual steps.
Если вы создаете приложение Electron, которое собираетесь упаковывать и распространять, оно должно быть подписано. The Electron ecosystem tooling makes codesigning your apps straightforward - this documentation explains how sign your apps on both Windows and macOS.
Signing & notarizing macOS builds
Preparing macOS applications for release requires two steps: First, the app needs to be code signed. Then, the app needs to be uploaded to Apple for a process called notarization, where automated systems will further verify that your app isn't doing anything to endanger its users.
To start the process, ensure that you fulfill the requirements for signing and notarizing your app:
- Зарегистрироваться в Apple Developer Program (требует оплату раз в год)
- Download and install Xcode - this requires a computer running macOS
- Generate, download, and install signing certificates
Electron's ecosystem favors configuration and freedom, so there are multiple ways to get your application signed and notarized.
Using Electron Forge
If you're using Electron's favorite build tool, getting your application signed and notarized requires a few additions to your configuration. Forge is a collection of the official Electron tools, using @electron/packager, @electron/osx-sign, and @electron/notarize under the hood.
Detailed instructions on how to configure your application can be found in the Signing macOS Apps guide in the Electron Forge docs.
Using Electron Packager
If you're not using an integrated build pipeline like Forge, you are likely using @electron/packager, which includes @electron/osx-sign and @electron/notarize.
If you're using Packager's API, you can pass in configuration that both signs and notarizes your application. If the example below does not meet your needs, please see @electron/osx-sign and @electron/notarize for the many possible configuration options.
const packager = require('@electron/packager')
packager({
dir: '/path/to/my/app',
osxSign: {},
osxNotarize: {
appleId: 'felix@felix.fun',
appleIdPassword: 'my-apple-id-password'
}
})
Signing Mac App Store applications
See the Mac App Store Guide.
Подписывание сборок для Windows
Using traditional certificates
Before you can code sign your application, you need to acquire a code signing certificate. Unlike Apple, Microsoft allows developers to purchase those certificates on the open market. They are usually sold by the same companies also offering HTTPS certificates. Prices vary, so it may be worth your time to shop around. Популярные реселлеры включают:
- Certum EV code signing certificate
- DigiCert EV code signing certificate
- Entrust EV code signing certificate
- GlobalSign EV code signing certificate
- IdenTrust EV code signing certificate
- Sectigo (formerly Comodo) EV code signing certificate
- SSL.com EV code signing certificate
It is important to call out that since June 2023, Microsoft requires software to be signed with an "extended validation" certificate, also called an "EV code signing certificate". In the past, developers could sign software with a simpler and cheaper certificate called "authenticode code signing certificate" or "software-based OV certificate". These simpler certificates no longer provide benefits: Windows will treat your app as completely unsigned and display the equivalent warning dialogs.
The new EV certificates are required to be stored on a hardware storage module compliant with FIPS 140 Level 2, Common Criteria EAL 4+ or equivalent. In other words, the certificate cannot be simply downloaded onto a CI infrastructure. In practice, those storage modules look like fancy USB thumb drives.
Many certificate providers now offer "cloud-based signing" - the entire signing hardware is in their data center and you can use it to remotely sign code. This approach is popular with Electron maintainers since it makes signing your applications in CI (like GitHub Actions, CircleCI, etc) relatively easy.
At the time of writing, Electron's own apps use DigiCert KeyLocker, but any provider that provides a command line tool for signing files will be compatible with Electron's tooling.
All tools in the Electron ecosystem use @electron/windows-sign and typically expose configuration options through a windowsSign property. You can either use it to sign files directly - or use the same windowsSign configuration across Electron Forge, @electron/packager, electron-winstaller, and electron-wix-msi.
Using Electron Forge
Electron Forge is the recommended way to sign your app as well as your Squirrel.Windows and WiX MSI installers. Detailed instructions on how to configure your application can be found in the Electron Forge Code Signing Tutorial.
Using Electron Packager
If you're not using an integrated build pipeline like Forge, you are likely using @electron/packager, which includes @electron/windows-sign.
If you're using Packager's API, you can pass in configuration that signs your application. If the example below does not meet your needs, please see @electron/windows-sign for the many possible configuration options.
const packager = require('@electron/packager')
packager({
dir: '/path/to/my/app',
windowsSign: {
signWithParams: '--my=custom --parameters',
// If signtool.exe does not work for you, customize!
signToolPath: 'C:\\Path\\To\\my-custom-tool.exe'
}
})
Using electron-winstaller (Squirrel.Windows)
electron-winstaller is a package that can generate Squirrel.Windows installers for your Electron app. This is the tool used under the hood by Electron Forge's Squirrel.Windows Maker. Just like @electron/packager, it uses @electron/windows-sign under the hood and supports the same windowsSign options.
const electronInstaller = require('electron-winstaller')
// NB: Use this syntax within an async function, Node does not have support for
// top-level await as of Node 12.
try {
await electronInstaller.createWindowsInstaller({
appDirectory: '/tmp/build/my-app-64',
outputDirectory: '/tmp/build/installer64',
authors: 'My App Inc.',
exe: 'myapp.exe',
windowsSign: {
signWithParams: '--my=custom --parameters',
// If signtool.exe does not work for you, customize!
signToolPath: 'C:\\Path\\To\\my-custom-tool.exe'
}
})
console.log('It worked!')
} catch (e) {
console.log(`No dice: ${e.message}`)
}
For full configuration options, check out the electron-winstaller repository!
Using electron-wix-msi (WiX MSI)
electron-wix-msi is a package that can generate MSI installers for your Electron app. This is the tool used under the hood by Electron Forge's MSI Maker. Just like @electron/packager, it uses @electron/windows-sign under the hood and supports the same windowsSign options.
import { MSICreator } from 'electron-wix-msi'
// Step 1: Instantiate the MSICreator
const msiCreator = new MSICreator({
appDirectory: '/path/to/built/app',
description: 'My amazing Kitten simulator',
exe: 'kittens',
name: 'Kittens',
manufacturer: 'Kitten Technologies',
version: '1.1.2',
outputDirectory: '/path/to/output/folder',
windowsSign: {
signWithParams: '--my=custom --parameters',
// If signtool.exe does not work for you, customize!
signToolPath: 'C:\\Path\\To\\my-custom-tool.exe'
}
})
// Step 2: Create a .wxs template file
const supportBinaries = await msiCreator.create()
// 🆕 Step 2a: optionally sign support binaries if you
// sign you binaries as part of of your packaging script
for (const binary of supportBinaries) {
// Binaries are the new stub executable and optionally
// the Squirrel auto updater.
await signFile(binary)
}
// Step 3: Compile the template to a .msi file
await msiCreator.compile()
For full configuration options, check out the electron-wix-msi repository!
Using Electron Builder
Electron Builder comes with a custom solution for signing your application. You can find its documentation here.
Using Azure Trusted Signing
Azure Trusted Signing is Microsoft's modern cloud-based alternative to EV certificates. It is the cheapest option for code signing on Windows, and it gets rid of SmartScreen warnings.
As of October 2025, Azure Trusted Signing is available to US and Canada-based organizations with 3+ years of verifiable business history and to individual developers in the US and Canada. Microsoft is looking to make the program more widely available. If you're reading this at a later point, it could make sense to check if the eligibility criteria have changed.
Using Electron Forge
Electron Forge is the recommended way to sign your app as well as your Squirrel.Windows and WiX MSI installers. Instructions for Azure Trusted Signing can be found here.
Using Electron Builder
The Electron Builder documentation for Azure Trusted Signing can be found here.
Signing Windows Store applications
See the Windows Store Guide.