O primeiro commit do repositório electron/electron foi em 13 de março de 20131.
Após 10 anos e 27,147 mais commits de 1192 contribuintes únicos, Electron se tornou uma das estruturas mais populares para construir aplicativos de desktop hoje. Esse marco é a oportunidade perfeita para celebrar e refletir sobre nossa jornada até agora, e para compartilhar o que aprendemos ao longo o caminho.
Nós não estaríamos aqui hoje sem todos que dedicaram seu tempo e seu esforço para contribuir com o projeto. Embora as contribuições de commits de código-fonte sejam sempre as mais visíveis, também devemos reconhecer o esforço das pessoas que relatam bugs, mantêm módulos de usuário, fornecem documentação e traduções, e participam na comunidade Electron em todo o ciberespaço. Todos os contributos são inestimáveis para nós, como mantenedores.
Antes de continuarmos com o resto do post: obrigado. ❤️
Como chegamos aqui?
Atom Shell foi construído como a espinha dorsal do GitHub Editor Atom, que foi lançado em beta público em Abril de 2014. Foi construído a partir do zero como uma alternativa aos frameworks baseados na web disponíveis no tempo (node-webkit e Chromium Embedded Framework). Ele tinha um recurso matador: incorporando Node.js e Chromium para fornecer um poderoso tempo de execução desktop para tecnologias web.
Dentro de um ano, Atom Shell começou a assistir a um enorme crescimento das capacidades e da popularidade. Grandes empresas, startups e desenvolvedores individuais também começaram a construir aplicativos com ele (alguns early adopters incluem Slack, GitKraken, e WebTorrent), e o projeto foi apropriadamente renomeado para Electron.
A partir daí, o Electron começou com força total e nunca parou. Aqui está uma olhada em nossa contagem semanal de downloads ao longo do tempo, cortesia de npmtrends.com:
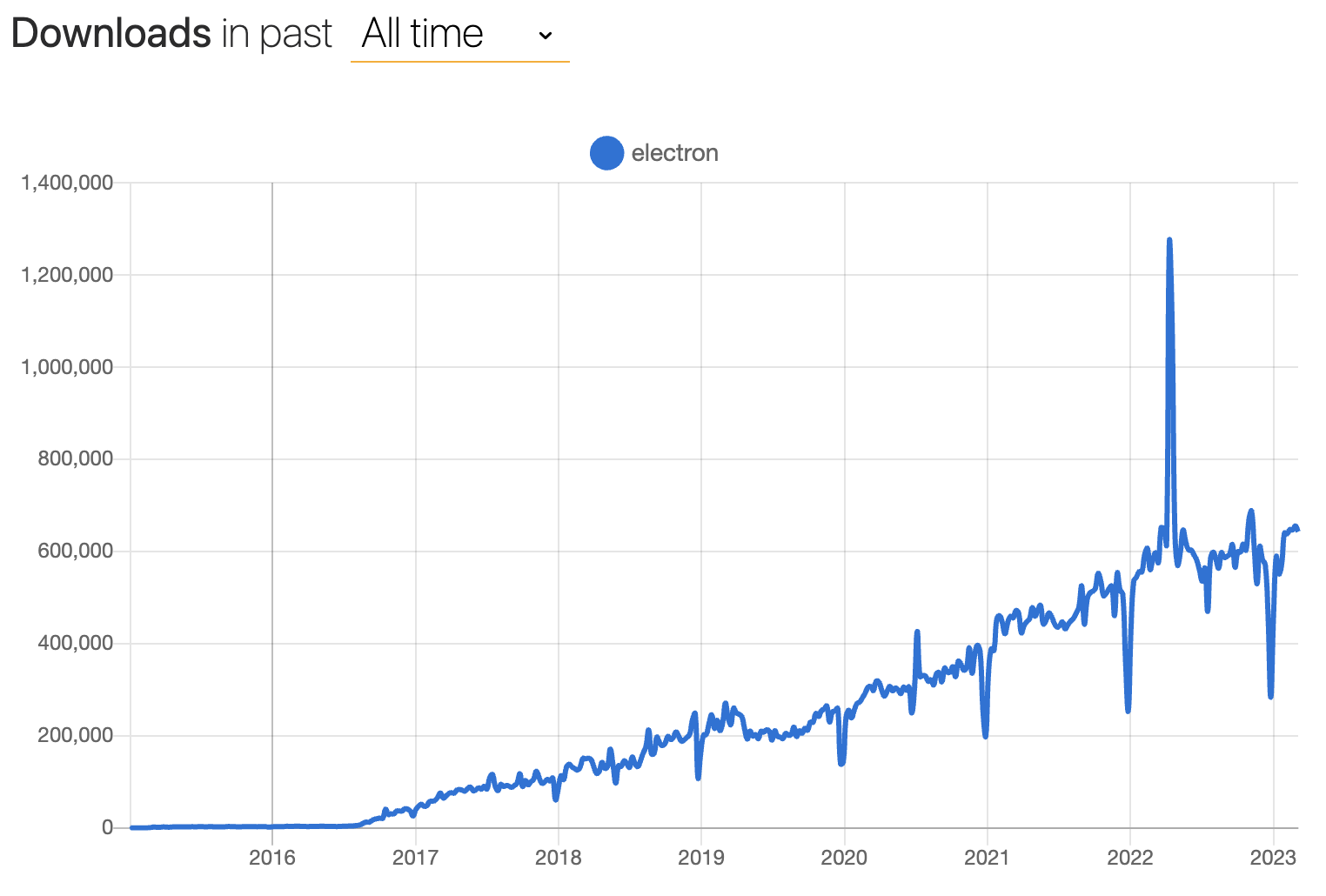
Electron v1 foi lançado em 2016, prometendo maior estabilidade da API e melhores documentos e ferramentas. Electron v2 foi lançado em 2018 e introduzido a versão semântica, tornando mais fácil para desenvolvedores Electron manter controle do ciclo de lançamento.
Por Electron v6, mudamos para uma cadência de lançamento maior de 12 semanas para combinar com a do Chromium. Esta decisão foi uma alteração na mentalidade do projeto, trazendo “ter a versão mais atualizada do Chromium ” de um nicho a ter uma prioridade. Isso reduziu a quantidade de dívida em tecnologia entre atualizações, tornando mais fácil para nós manter o Electron atualizado e seguro.
Desde então, temos funcionado como uma máquina bem oleada, lançando uma nova versão do Electron no mesmo dia que cada versão estável do Chromium. Quando o Chromium acelerou seu cronograma de lançamentos para 4 semanas em 2021, conseguimos simplesmente dar de ombros e aumentar nossa cadência de lançamentos para 8 semanas de acordo.
Agora estamos no Electron v23 (e contando), e ainda estamos dedicados a construir o melhor tempo de execução para construir aplicativos desktop multiplataforma. Mesmo com o boom das ferramentas de desenvolvedor de JavaScript em últimos anos, Electron continuou a ser uma paisagem estável e testada por batalhas do framework do aplicativo para desktop. Aplicativos Electron atualmente são onipresentes: você pode programar com o Visual Studio Code, projetar com Figma, se comunicar com o Slack, e fazer notas com Notion (entre muitos outros casos de uso). Estamos incrivelmente orgulhosos desta conquista e gratos a todos que a tornaram possível.
O que aprendemos ao longo do caminho?
O caminho para o marco da década tem sido longo e ventoso. Aqui estão algumas coisas-chave que nos ajudaram a administrar um projeto de código aberto grande e sustentável.
Um desafio que tivemos que superar foi lidar com a direção de longo prazo do projeto uma vez que o Electron explodiu na popularidade. Como lidamos com ser uma equipe de algumas dezenas de engenheiros distribuídos por empresas, países e fusos horários?
Nos primeiros dias, o grupo de mantenedores do Electron baseou-se em coordenação informal, que é rápido e leve para projetos menores, mas não escala para uma colaboração mais ampla. Em 2019, mudamos para um modelo de governança onde diferentes grupos de trabalho têm áreas formais de responsabilidade. Isto tem sido instrumental na racionalização de processos e atribuição de porções de propriedade do projeto a mantenedores específicos. Qual é a responsabilidade de cada grupo de trabalho (WG) actualmente?
- Obter lançamentos do Electron rápido (Releases WG)
- Atualizar o Chromium e o Node.js (Atualiza o WG)
- Supervisão do design da API pública (Grupo de Trabalho de API)
- Manter o Electron seguro (WG de segurança)
- Manter o site, a documentação e a ferramenta (Ecosystem WG)
- Alcance da Comunidade e corporativa (Outreach WG)
- Moderação comunitária (Community & Segurança WG)
- Manutenção de nossa infraestrutura construtiva, mantenedores de ferramentas e serviços de nuvem (Infraestrutura de WG)
Por volta do mesmo período em que mudamos para o modelo de governança, transferimos a propriedade do Electron do GitHub para a OpenJS Foundation. Embora a equipe central original ainda trabalhe na Microsoft hoje, eles são apenas uma parte de um grupo maior de colaboradores que compõem a governança do Electron.2
Embora esse modelo não seja perfeito, ele nos serviu bem durante uma pandemia global e desafios econômicos contínuos. Indo em frente, nós planejamos renovar a carta de governança para nos guiar durante a segunda década da Electron.
Comunidade
A parte da comunidade de código aberto é difícil, especialmente quando sua equipe de Outreach é uma dúzia de engenheiros em um casaco de trincheiras que diz "gerente da comunidade". Dito isso, ser um grande projeto de código aberto significa que temos muitos usuários, e utilizar sua energia para o Electron construir um ecossistema da userland é uma parte crucial para sustentar a saúde do projeto.
O que temos estado a fazer para desenvolver a nossa presença na comunidade?
Criando comunidades virtuais
- Em 2020, lançamos o servidor da nossa comunidade do Discord. Anteriormente tínhamos uma secção no fórum do Atom, mas decidiu ter uma plataforma de mensagens mais informal para ter um espaço para discussões entre mantenedores e desenvolvedores Electron e para ajuda geral na depuração.
- Em 2021, estabelecemos o grupo de usuários Electron China com a ajuda da @BlackHole1. Este grupo tem sido instrumental no crescimento do Electron em usuários da cena tecnológica da China, proporcionando um espaço para eles colaborarem em ideias e discuta o Electron fora de nossos espaços em inglês. Nós também gostaríamos de agradecer à cnpm pelo seu trabalho de apoio aos lançamentos noturnos da Electron, em seu espelho Chinês para o npm.
Participando de programas de alta visibilidade de código aberto
- Temos comemorado o Hacktoberfest todos os anos desde 2019. O Hacktoberfest é uma celebração anual de código aberto organizada pela DigitalOcean, e todos os anos recebemos dezenas de colaboradores entusiasmados que buscam deixar sua marca no software de código aberto.
- Em 2020, participamos da iteração inicial da Google Season of Docs, onde trabalhamos com @bandantonio para retrabalhar o novo fluxo de tutorial do Electron.
- Em 2022, mentoramos um aluno do "Google Summer of Code" pela primeira vez. @aryanshridhar fez um ótimo trabalho para refatorar a principal lógica de carregamento de versão do Electron Fiddle e migrar o seu empacotamento para webpack.
Automatizar todas as coisas!
Hoje, a governaça do Electron conta com cerca de 30 mantenedores ativos. Menos de metade de nós somos colaboradores a tempo integral contribuidores, o que significa que há muito trabalho a fazer. Qual é o nosso truque para manter tudo funcionando sem problemas? O nosso lema é que os computadores são baratos, e o tempo humano é caro. De forma típica de engenheiro, nós desenvolvemos um conjunto de ferramentas automatizadas de suporte para tornar nossas vidas mais fáceis.
Not Goma
A base de código central do Electron é um gigante de código C++, e os tempos de compilação sempre foram um fator limitante na velocidade com que podemos entregar correções de falhas e novos recursos. In 2020, we deployed Not Goma, a custom Electron-specific backend for Google’s Goma distributed compiler service. Não é um processo de compilação do (Goma) que solicita solicitações de máquinas autorizadas do usuário e distribui o processo por centenas de núcleos do backend. Ele também armazena em cache o resultado da compilação, para que qualquer outra pessoa que compile os mesmos arquivos precisem
Desde o lançamento Não Goma, os tempos de compilação para mantenedores diminuíram de uma escala de horas para minutos. Uma conexão estável com a internet tornou-se o requisito mínimo de contribuidores para compilar o Electron!
Se você é um colaborador de código aberto, pode tentar o cache não somente de leitura do Goma, que é disponível por padrão com Electron Build Tools.
Fator de Autenticação Contínua
Continuous Factor Authentication (CFA) é uma camada de automação em torno do sistema de autenticação de dois fatores (2FA) do npm, que combinamos com o semantic-release para gerenciar lançamentos seguros e automatizados de nossos vários pacotes @electron/ do npm.
Embora o semantic-release já automatize o processo de publicação de pacotes npm, ele exige desativar a autenticação de dois fatores ou passar um token secreto que contorna essa restrição.
Construímos o CFA para fornecer uma senha de uso único baseada em tempo (TOTP) para o 2FA do npm em tarefas de CI arbitrárias, permitindo-nos aproveitar a automação do semantic-release enquanto mantemos a segurança adicional da autenticação de dois fatores.
Usamos o CFA com um front-end de integração do Slack, permitindo que os mantenedores validem a publicação do pacote de qualquer dispositivo em que o Slack esteja ativado, contanto que tenham seu gerador TOTP útil.
Se você quer testar CFA em seus próprios projetos, confira o repositório do GitHub ou a documentação! Se você usar o CircleCI como seu provedor de CI, também temos um orb para rapidamente encontrar um projeto com CFA.
Sheriff
Sheriff é uma ferramenta de código aberto que escrevemos para automatizar a ferramenta gerenciamento de permissões em todo o GitHub, Slack e Google Workspace.
A proposta de valor-chave do Sherif é que a gestão de permissão deve ser um processo transparente. Ele usa um único arquivo de configuração YAML que designa permissões através de todos os serviços listados acima. Com o Sheriff, obter o status de colaborador em um repositório ou criar uma nova lista de e-mails é tão fácil quanto obter um PR aprovado e mesclado.
O Sheriff também possui um registro de auditoria que posta no Slack, alertando os administradores quando atividades suspeitas ocorrem em qualquer lugar na organização Electron.
…e todos os nossos bots no GitHub
O GitHub é uma plataforma com a rica extensibilidade da API e um framework de aplicativo de primeiro grupo chamado Probot. Para nos ajudar a focar nas partes mais criativas do nosso trabalho, construímos um conjunto de bots menores que nos ajudam a fazer o trabalho sujo. Eis alguns exemplos:
- Sudowodo automatiza o processo de lançamento do Electron do início ao fim, desde o início das compilações até o upload dos arquivos de lançamento para o GitHub e npm.
- Trop automatiza o processo de backporting para o Electron, tentando aplicar patches (usando cherry-pick) em branches de versões anteriores com base nos labels das Pull Requests (PRs) do GitHub.
- Roller automatiza as atualizações do Chromium do Electron e das dependências do Node.js.
- Cation é nosso bot de verificação de status para electron/electron PRs.
Ao todo, nossa pequena família de bots nos deu um grande impulso na produtividade do desenvolvedor!
What’s next?
À medida que entramos em nossa segunda década como um projeto, você deve estar perguntando: o que vem por aí com o Electron?
Vamos continuar em sincronia com a cadência de lançamentos do Chromium, lançando novas versões principais do Electron a cada 8 semanas, mantendo o framework atualizado com o que há de mais recente na plataforma web e no Node.js, ao mesmo tempo em que mantemos estabilidade e segurança para aplicativos de nível empresarial.
Normalmente anunciamos notícias sobre iniciativas futuras quando elas se tornam concretas. Se você quiser se manter informado sobre as versões futuras, recursos e atualizações gerais do projeto, você pode ler nosso blog e seguir nossos perfis de mídia social (Twitter e Mastodon)!









