Reflecting on the improvements and changes in Electron's developer ecosystem in 2023.
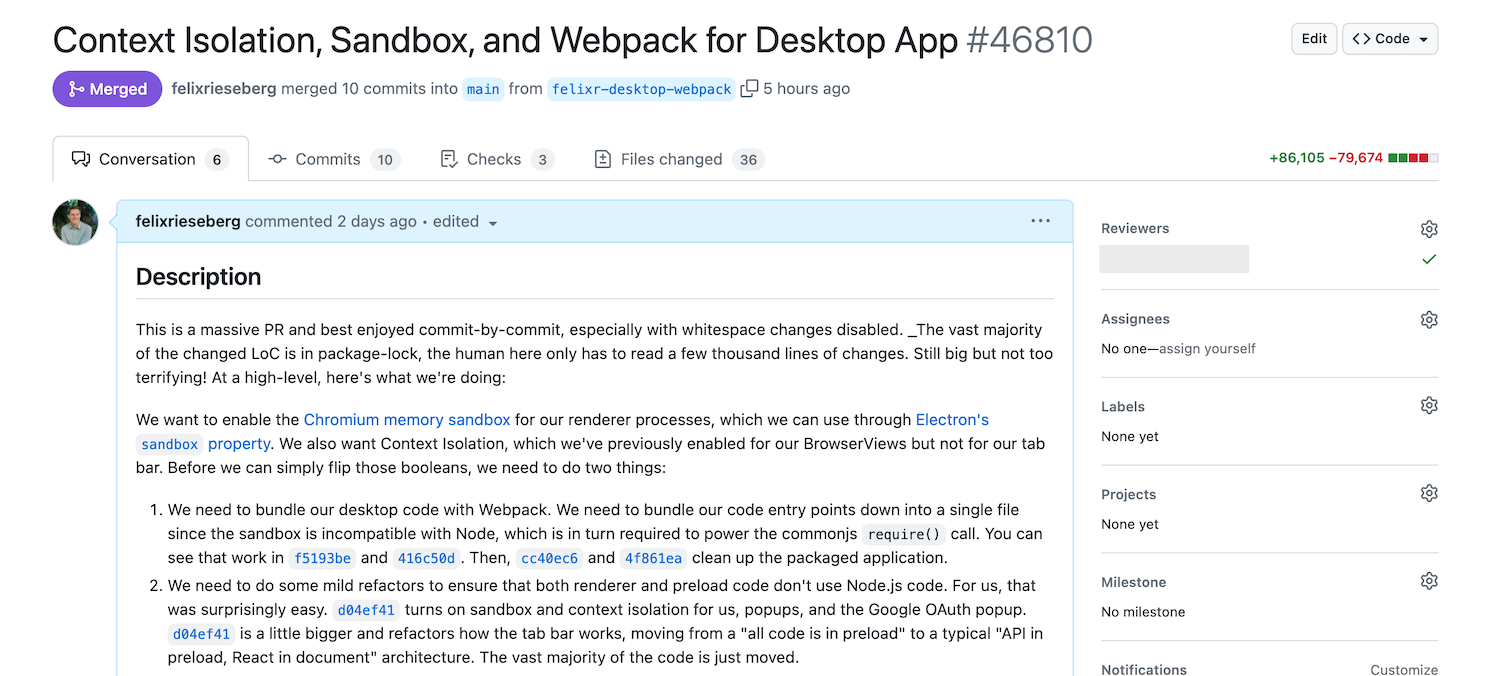
In the past few months, we've been cooking up some changes across the Electron ecosystem to supercharge the developer experience for Electron apps! Here’s a swift rundown of the latest additions straight from Electron HQ.
Electron Forge 7 and beyond
Electron Forge 7 — the newest major version of our all-in-one tool for packaging and distributing Electron applications — is now available.
While Forge 6 was a complete rewrite from v5, v7 is smaller in scope but still contains a few breaking changes. Going forward, we will continue to publish major versions of Forge as breaking changes need to be made.
For more details, see the full Forge v7.0.0 changelog on GitHub.
Wichtige Änderungen
- Switched to
notarytool for macOS notarization: As of 2023-11-01, Apple sunset the legacy altool for macOS notarization, and this release removes it from Electron Forge entirely.
- Minimum Node.js increased to v16.4.0: With this release, we’ve set the minimum required Node.js version to 16.4.0.
- Dropped support for
electron-prebuilt and electron-prebuilt-compile: electron-prebuilt was the original name for Electron’s npm module, but was replaced by electron in v1.3.1. electron-prebuilt-compile was an alternative to that binary that came with enhanced DX features, but was eventually abandoned as a project.
Highlights
- Google Cloud Storage publisher: As part of our push to better support static auto updating, Electron Forge now supports publishing directly to Google Cloud Storage!
- ESM forge.config.js support: Electron Forge now supports ESM
forge.config.js files. (P.S. Look forward to ESM entrypoint support in Electron 28.)
- Makers now run in parallel: In Electron Forge 6, Makers ran sequentially for ✨ legacy ✨ reasons. Since then, we’ve tested out parallelization for the Make step with no adverse side effects, so you should see a speed-up when building multiple targets for the same platform!
🙇 Big thanks to mahnunchik for the contributions for both the GCS Publisher and ESM support in Forge configurations!
Better static storage auto updates
Squirrel.Windows and Squirrel.Mac are platform-specific updater technologies that back Electron’s built-in autoUpdater module. Both projects support auto updates via two methods:
- A Squirrel-compatible update server
- A manifest URL hosted on a static storage provider (e.g. AWS, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, etc.)
The update server method has traditionally been the recommended approach for Electron apps (and provides additional customization of update logic), but it has a major downside—it requires apps to maintain their own server instance if they are closed-source.
On the other hand, the static storage method has always been possible, but was undocumented within Electron and poorly supported across Electron tooling packages.
With some great work from @MarshallOfSound, the update story for serverless automatic app updates has been drastically streamlined:
- Electron Forge’s Zip and Squirrel.Windows makers can now be configured to output
autoUpdater-compatible update manifests.
- A new major version of
update-electron-app (v2.0.0) can now read these generated manifests as an alternative to the update.electronjs.org server.
Once your Makers and Publishers are configured to upload update manifests to cloud file storage, you can enable auto updates with only a few lines of configuration:
const { updateElectronApp, UpdateSourceType } = require('update-electron-app');
updateElectronApp({
updateSource: {
type: UpdateSourceType.StaticStorage,
baseUrl: `https://my-manifest.url/${process.platform}/${process.arch}`,
},
});
The @electron/ extended universe
When Electron first started, the community published many packages to enhance the experience of developing, packaging, and distributing Electron apps. Over time, many of these packages were incorporated into Electron’s GitHub organization, with the core team taking on the maintenance burden.
In 2022, we began unifying all these first-party tools under the @electron/ namespace on npm. This change means that packages that used to be electron-foo are now @electron/foo on npm, and repositories that used to be named electron/electron-foo are now electron/foo on GitHub. These changes help clearly delineate first-party projects from userland projects. This includes many commonly used packages, such as:
@electron/asar@electron/fuses@electron/get@electron/notarize@electron/osx-sign@electron/packager@electron/rebuild@electron/remote@electron/symbolicate-mac@electron/universal
Going forward, all first-party packages we release will also be in the @electron/ namespace. There are two exceptions to this rule:
- Electron core will continue to be published under the
electron package.
- Electron Forge will continue to publish all of its monorepo packages under the
@electron-forge/ namespace.
⭐ During this process, we also accidentally took the electron/packager repository private, which has the unfortunate side effect of erasing our GitHub star count (over 9000 before the erasure). If you are an active user of Packager, we’d appreciate a ⭐ Star ⭐!
Introducing @electron/windows-sign
Starting on 2023-06-01, industry standards began requiring keys for Windows code signing certificates to be stored on FIPS-compliant hardware.
In practice, this meant that code signing became a lot harder for apps that build and sign in CI environments, since many Electron tools take in a certificate file and password as config parameters and attempt to sign from there using hardcoded logic.
This situation has been a common pain point for Electron developers, which is why we have been working on a better solution that isolates Windows code signing into its own standalone step, similar to what @electron/osx-sign does on macOS.
In the future, we plan on fully integrating this package into the Electron Forge toolchain, but it currently lives on its own. The package is currently available for installation at npm install --save-dev @electron/windows-sign and can used programmatically or via CLI.
Please try it out and give us your feedback in the repo’s issue tracker!
What's next?
We'll be entering our annual December quiet period next month. While we do, we'll be thinking about how we can make the Electron development experience even better in 2024.
Is there anything you'd like to see us work on next? Gib uns Bescheid!